What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation is an issue found in people of all ages. It refers to the colouring of the skin, hair, and eyes, which is caused by melanin, a pigment produced by specialised skin cells called melanocytes. The amount of melanin in the skin determines its colour. Melanin is usually distributed evenly, but sometimes there are spots or patches with more melanin. There are different types of pigmentation, including hyperpigmentation (dark patches caused by excess melanin), hypopigmentation (lighter patches due to reduced melanin), melasma (hormonal pigmentation often seen in pregnant women), and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (caused by skin trauma or inflammation).
These spots can be freckles, age spots, or melasma. However, there is a lot of misinformation spreading about pigmentation which leads to confusion and ineffective remedies. Let’s uncover these myths about pigmentation and present the facts. We will also explore the types of pigmentation, causes of hyperpigmentation, and PRP treatment as an advanced solution for skin discolouration instead of ineffective remedies that are practised.
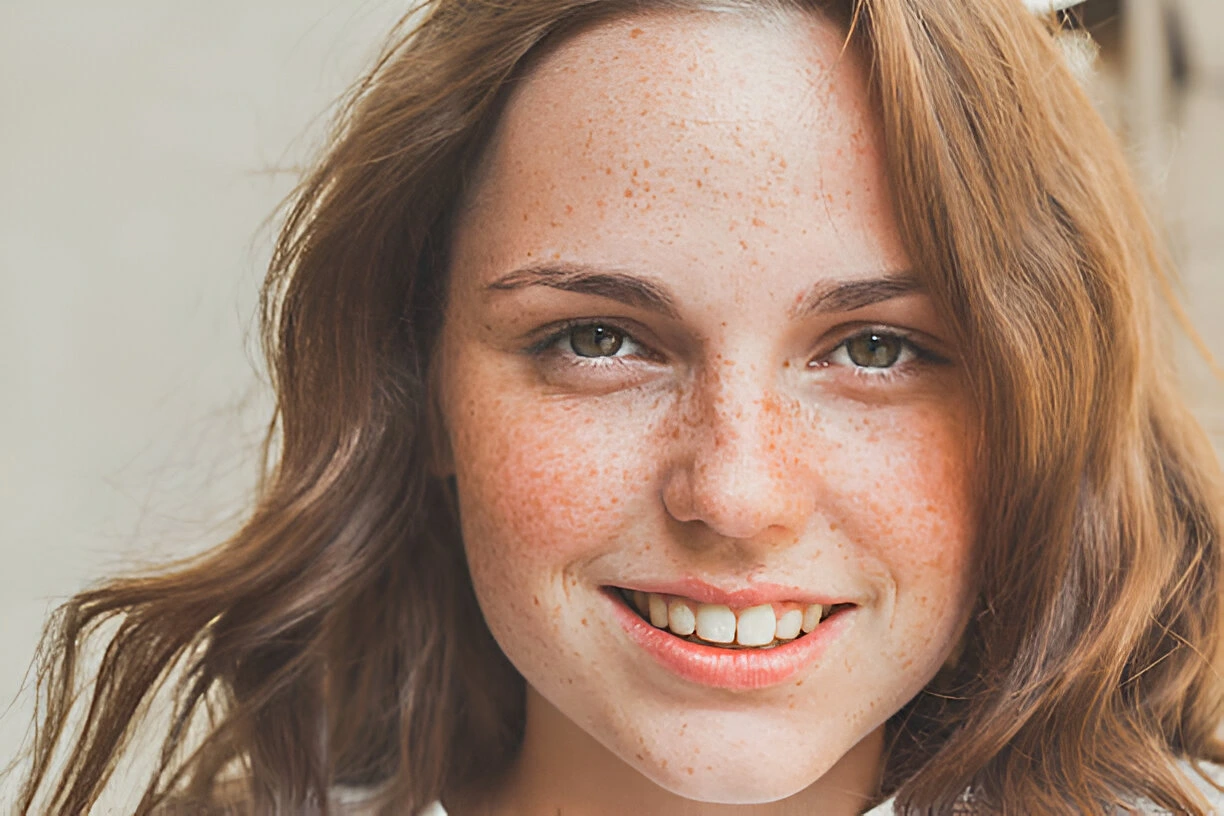

Myths & Facts About Pigmentation
Pigmentation Only Affects Dark Skin
Reality – No, pigmentation issues can affect people of all skin types, but they are more noticeable in darker skin. Fair-skinned individuals can also experience pigmentation issues such as freckles, age spots, and sun-induced discolouration
Hyperpigmentation is Caused by Sun Exposure
Reality – While Sun exposure is the major reason for hyperpigmentation, there are many causes of Hyperpigmentation such as hormonal changes, inflammation, genetics, medications, and even skincare products can lead to pigmentation issues.
Hyperpigmentation Will Go Away on Its Own
Reality – Yes, sometimes hyperpigmentation goes on its own depending on its severity. Some types of pigmentation, like PIH may fade over time. But without proper care and sun protection, pigmentation can persist and even worsen.
Scrubbing Skin Can Remove Pigmentation
Reality – Over-exfoliation can damage the skin barrier, leading to increased inflammation and triggering more melanin production, which can make pigmentation worse.
All Pigmentation is the Same
Reality – Not all pigmentation is the same there are various types of pigmentation and each requires a specific approach to treatment. Some common types include Melasma, Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation, and Age Spots.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by to overproduction of melanin, which is responsible for skin colour. Some common causes of hyperpigmentation are Sun Exposure – UV rays from the sun trigger melanin production, Hormonal Changes – Pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations, and thyroid disease can all cause hyperpigmentation, Aging -As we age, our skin’s ability to repair itself slows down, resulting in pigmentation issues, Genetics – Genes influence skin tone, and some people are more likely to produce more melanin and Medications.
Types of Pigmentation & How to Identify?
Melasma
It is a form of pigmentation that seems dark, with irregular patches mainly seen on the facial area, such as the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip. Highly triggered due to hormonal changes such as pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone therapy and sun exposure worsens melasma, making sunscreen and protective skincare crucial.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
Occurs after skin injury like acne, burns, cuts, or aggressive cosmetic treatments and looks like dark patches at the site of healed inflammation, Just like Melasma, it affects all skin types and is common for darker skin.
Freckles
Freckles are brown patches which are developed due to sun exposure common in fair-skinned individuals and are caused by an increase in melanin production.
Age Spots
Appear as flat, brown, or black spots, primarily on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms and it’s common in older adults.
Hypopigmentation
It occurs when the skin loses melanin, leading to lighter patches. Unlike hyperpigmentation, which involves excess melanin, hypopigmentation results from a lack of pigment in certain areas.
How to Prevent and Treat Hyperpigmentation Effectively
Avoid direct sunlight
Wearing sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is crucial in preventing pigmentation from worsening. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially if outdoors. Minimize the sun exposure.
Limit touching your skin.
Scratching or picking a mosquito bite or a spot can result in inflammation and lead to darker pigmentation on your face, so it’s best to avoid touching your skin. When you do touch your skin, for example when applying your skin care or makeup, make sure you wash your hands first.
Use Targeted Skincare Products
Vitamin C: Helps brighten the skin and reduce dark spots.
Niacinamide: Reduces inflammation and regulates melanin production.
Retinoids: Promote skin cell turnover, helping to fade pigmentation.
Hydroquinone: A well-known skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production.
Understanding the types of pigmentation, knowing the causes of hyperpigmentation, and opting for scientifically proven treatments like PRP treatment can help you achieve clearer, healthier skin. Don’t fall for myths—trust expert-backed solutions to manage and treat pigmentation effectively.
At Dermis Oracle, we offer advanced skincare solutions, including PRP treatment, chemical peels, and personalized skincare regimens to help you combat pigmentation issues. Book a consultation with us today and take the first step toward radiant, even-toned skin!